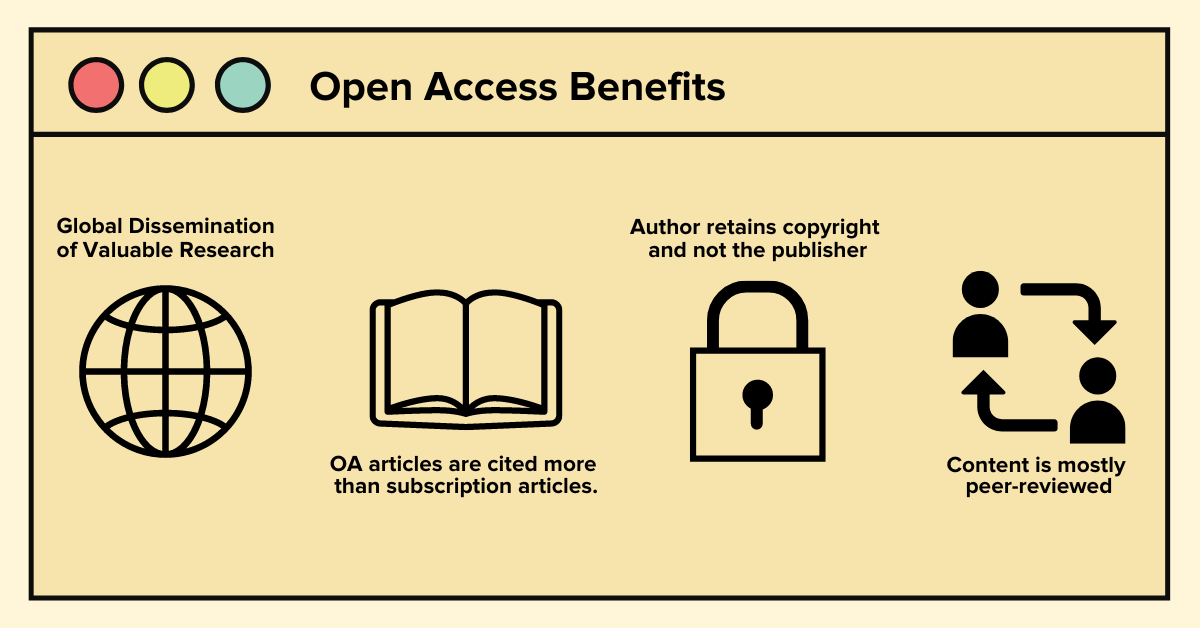
One of the most defining aspects of academic research writing is a demonstration of research-oriented findings. Referring to credible sources and data is made possible through the concept of citations. In this blog, we’ll equip you with citation knowledge across multiple different formats and aid in understanding the purpose of each one.
The purpose of citations
When you search the definition of the term ‘citation’ on google, you’re met with the following description: a quotation from or reference to a book, paper, or author, especially in a scholarly work. Citing sources has multiple purposes, the primary focus is to give credit to the original author. When writing a specialised research paper, the author will cite external sources when referencing the material in their own work to establish strength, transparency and authority within their research.
This positions their work in a specific context to depict their stance in the larger discussion. Citations also serve as an efficient way to provide references to others wanting to explore the subject or even use them within their own academic research papers. Overall, citing establishes an important roadmap in the research process.
Why are there different types of citations?
Different citation formats are utilised across different disciplines. While it might be convenient to have one universal citation format, it is not possible because different fields focus on unique information within their respective research; this requires citation formats to be tailored to the field’s primary focus.
The APA (American Psychological Association) citation format is utilised in social sciences like psychology, sociology, anthropology as well as education. Moreover, the MLA (Modern Language Association) citation format is largely used within humanities and the Chicago citation format is applied in the fields of Business, History & Fine Arts. Finally, the Harvard citation format is primarily used in education.
Citing in APA Referencing Format
APA (American Psychological Association) referencing style is a widely used referencing style in social science disciplines, such as psychology, sociology, and education. The style is characterised by the use of in-text citations, which typically include the author’s last name and the year of publication of the source being cited.
The APA style requires a detailed reference list, which includes all sources referenced in the text. The reference list is arranged alphabetically by the author’s last name, and each entry provides comprehensive information about the source, including the title, publisher, and publication date.
- Book: Author, A.A. (Year of Publication). The Title of work. Publisher City, State: Publisher.
- Journal Article: Last name, Initials. (Year). Article title. Journal Name, Volume(Issue), Page range. DOI or URL
- Magazine: Author, A.A. (Year, a month of Publication). Article title. Magazine Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Newspaper: Author, A.A. (Year, Month Date of Publication). Article title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
- Website: Author, A.A. (Year, Month Date of Publication). Article title. Retrieved from URL
Citing in MLA Referencing Format
MLA (Modern Language Association) referencing style is a popular method of citing sources used in academic writing, particularly in the humanities. The style is characterised by the use of in-text citations, which typically include the author’s last name and the page number(s) of the source being cited. The MLA style also requires a comprehensive list of Works Cited at the end of the document, which includes all sources referenced in the text. The Works Cited page is arranged alphabetically by the author’s last name or, if there is no author, by the first word of the title.
- Book: Last Name, First Name. Book Title. Publisher City: Publisher Name, Year Published. Medium.
- Journal Article: Author last name, First name. “Article Title.” Journal Name, vol. Volume, no. Issue, Month Year, Page range. DOI or URL.
- Magazine: Last Name, First Name. “Article Title.” Magazine Name Publication Date: Page Numbers. Medium.
- Newspaper: Last Name, First Name. “Article Title.” Newspaper Name Publication Date: Page Numbers. Medium.
- Website: Last Name, First Name. “Page Title.” Website Title.Sponsoring Institution/Publisher. Publication Date: Page Numbers. Medium.
Citing in Harvard Referencing Format
Harvard style referencing, also known as author-date referencing, is a widely used referencing system that originated from Harvard University. It is a method of acknowledging sources of information in academic writing, by citing the author’s last name and the year of publication in the text. Harvard referencing style also requires a detailed list of references at the end of the document, arranged alphabetically by the author’s last name, which includes all the sources cited in the text. This style of referencing is used in many disciplines, including the social sciences, humanities, and natural sciences.
- Journal Articles: Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) ‘Title of article’, Title of Journal, volume number (issue number), page reference. If accessed online: Available at: DOI or URL (if required) (Accessed: date).
- Books: Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) Title. Edition if later than first. Place of publication: publisher. Series and volume number if relevant.
- Newspaper Article: Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) ‘Title of article’, Title of Newspaper, Day and month, Page reference.
- Online Newspaper Article: Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) ‘Title of article’, Title of Newspaper, Day and month, Page reference if available. Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
- Website: Surname, Initial. (Year that the site was published/last updated) Title of web page. Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Citing in Chicago Referencing Format
The Chicago referencing format is commonly used in the fields of Business, History and Fine Arts. It offers two main citation styles: the notes and bibliography style and the author-date style.
The notes and bibliography style involves the use of footnotes to provide brief citations within the text and a corresponding bibliography at the end of the document. In contrast, the author-date style involves in-text citations that include the author’s last name and the date of publication. A comprehensive reference list is also required at the end of the document.
- Journal Article: Author last name, First name. “Article Title.” Journal Name Volume, no. Issue (Month or Season Year): Page range. DOI or URL.
- Book: Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher City: Publisher Name, Year Published.
- Magazine: Last Name, First Name. Article title. Magazine Title, Month Date, Year of publication.
- Newspaper: Last Name, First Name. “Article Title.” Newspaper Name, Publication Date.
- Website: Last Name, First Name. “Page Title.” Website Title. Web Address (retrieved Date Accessed).
Citations and referencing bring attention to details within each format. While it is a time-consuming section to fulfill in an academic paper, it’s also an important skill to have as a researcher, to be able to dissect other research papers and build an authoritative and strengthened academic paper with your own research. Understanding which citation format is best suited for your discipline is equally important; this citation pocket guide covered the 4 commonly utilised citation styles which are APA, MLA, Harvard and Chicago.
Discover an array of academic resources now on Zendy where you can read through research worry-free because we offer automatic citations across all our books, journal articles, proceedings and more.